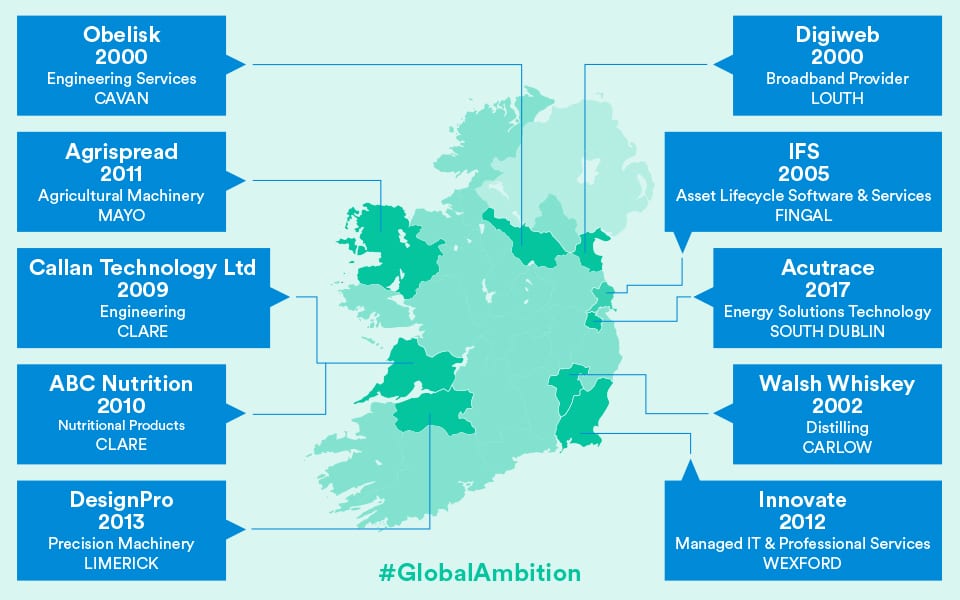
GDPR and Data transfer to or through the UK
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) came into force on 25 May 2018 and unifies data protection law throughout the EU. It gives individuals control over their personal data and requires businesses and other organisations to put in place processes that protect and safeguard that data. The regulation also addresses the transfer of personal data outside the EU and EEA.
Dealing with the UK, USA and other third countries
GDPR came into sharp focus this year as a result of the UK’s withdrawal from the EU. GDPR still applies in the UK, however as it is now a third country it is subject to the GDPR rules governing the transfer of data outside the EU and EEA.
Data transfer to/through the UK
The first thing for firms to do is to establish exactly where their data goes. Companies may not realise that their cloud storage provider is actually located in Britain or Northern Ireland. Their pension schemes, payroll, healthcare plans may all be run out of the UK and involve the regular transfer of personal data. Workplace benefits databases could also be held in Britain or Northern Ireland. Even translation services might be covered if personal data is included in the material to be translated.
Having established that data is being transferred to the UK, the next step is to decide if that needs to continue. There may be options to look for another service provider in Ireland or another EU Member State and these should be explored.
Standard Contractual Clauses
If it is not possible or if it is too difficult to take this option, there is a ready solution to hand. There is a tool that can be used to solve this problem and it is available on the Data Protection Commission website. It is known as the standard contractual clauses (SCCs). This is a set of off-the-shelf clauses developed by the European Commission and which are recognised as an appropriate safeguard to ensure that firms remain compliant with GDPR.
The SCCs are already written and only require firms to fill in the blanks with their details. They can be appended to existing contracts and come into force when both parties sign them. Once signed, this enables firms to continue transferring data to the UK in full compliance with GDPR, and people still have their rights.
The data subject is also given certain specific rights under the SCCs even though they are not party to the relevant contract. Firms are also advised to update their privacy statements to indicate that the data is transferring to the UK under the terms of the SCCs.
The SCCs will cover most situations, but there are certain more complex cases where they may not apply. These are relatively rare, but firms in doubt should consult the Data Protection Commission or seek their own legal advice to check out their particular situation.
There are also certain situations where the data transfer is not covered by contract. These include cases where data is being transferred from a UK Controller to an Irish processor for processing and then transferred back to the Controller. This has been a relatively routine process up until now, as the data remained within the EU at all times. The best advice for firms based in Ireland who find themselves in this situation is to look at the clauses within the SCCs and insert them into the service level agreement governing the activity. This will demonstrate an intention to be GDPR compliant in the new situation.
The same will apply to Irish shared services centres carrying out global back and middle office functions for multinational parents. They should update the terms of service to UK-based affiliates to include the SCCs.
Data Protection Policies
Some very large organisations use what are known as Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs). These are legally binding internal codes of conduct operating within a multinational group, which applies to transfers of personal data from the group’s EEA entities to the group’s non-EEA entities. The approval of BCRs can take a significant period of time and also, given the cost and complexity of BCRs, they are not a suitable transfer tool for most Irish companies.
The only remaining questions for Irish firms transferring data to the UK concern adequacy. Certain ‘third countries’, such as Japan, have received what is known as an ‘adequacy decision’ from the European Commission. This allows a cross-border personal data transfer from the EU to that country because it has been determined to have an adequate level of data protection safeguards compared to the EU. It could take some time before the European Commission completes its negotiations with the UK Government in order to deem the UK adequate as a jurisdiction to which data can be transferred under GDPR. Therefore, companies need to explore the options available to them when transferring data to the UK.







 CFO Greg Stafford said, “Diabetes is a massive global epidemic, with more than 400 million people suffering from the condition. We have the potential to make an extraordinary impact on the incidence of diabetes as Nuritas has identified and unlocked bioactive peptides with the potential to prevent this condition. We are honoured to have received a multimillion euro
CFO Greg Stafford said, “Diabetes is a massive global epidemic, with more than 400 million people suffering from the condition. We have the potential to make an extraordinary impact on the incidence of diabetes as Nuritas has identified and unlocked bioactive peptides with the potential to prevent this condition. We are honoured to have received a multimillion euro